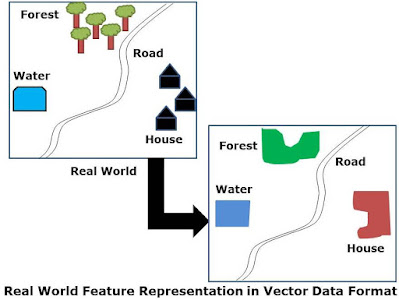
Vector Data Model
- Point
- Line
- Polygon
- Point- Hospitals, Wells etc.
- Line- Highway, River, Canal etc.
- Polygon- Forest, Agri Land, Urban Area etc.
- City: Name, Population, State
- Wells: Village, Depth
- Highway: Type, Number
- River: Name, Length
Vector Data Representation
- Node
- Vertex
- 0-Cell
- An edge
- Link
- Chain
- 1-Cell
- Area
- Region
- Zone
- 2-Cell
Point& Line Features
Polygon Features
Vector Data Advantages
- It represents more maps like in compare to raster data as it is more accurate and pleasing to eyes.
- Vector data is very high resolution and magnification does not affect display quality of data.
- Vector data require less storage space compare to raster data.
- Vector data are more users friendly and can be understood by public better than raster data.
- Vector data can also be represented topologically and allows analysis using topological data.
Vector Data Limitations
- Data formats may be more difficult to manage than raster format.
- Spatial data stored as long lists of coordinates, which is easier for computer to understand but difficult for users to understand and edit.
- Vector format creation is more expensive.
- Vector data processes of GIS are more difficult to learn
- Topology concept of GIS is difficult to understand.
- Raster data are easily availability compare to vector data.