Principle of interpretation of aerial photographs and satellite images
- The aerial and regional perspective
- The three dimensional depth perspective in the form of DEM
- Knowledge beyond our human visual perception
- The ability to obtain a historical image record to document change through Mapping
- Aerial photographs and satellite image
- Principle
- Interpretation
Aerial photographs and satellite image
Principle
Interpretation
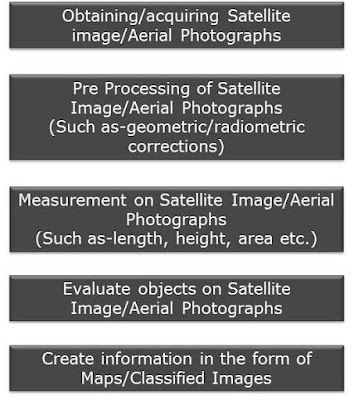
tableau online training in hyderabad
adana escort – adıyaman escort – afyon escort – aksaray escort – antalya escort – aydın escort – balıkesir escort – batman escort – bitlis escort – burdur escort – bursa escort – diyarbakır escort – edirne escort – erzurum escort – eskişehir escort – eskişehir escort – eskişehir escort – eskişehir escort – gaziantep escort – gebze escort – giresun escort – hatay escort – ısparta escort – karabük escort – kastamonu escort – kayseri escort – kilis escort – kocaeli escort – konya escort – kütahya escort – malatya escort – manisa escort – maraş escort – mardin escort – mersin escort – muğla escort – niğde escort – ordu escort – osmaniye escort – sakarya escort – samsun escort – siirt escort – sincan escort – tekirdağ escort – tokat escort – uşak escort – van escort – yalova escort – yozgat escort – urfa escort – zonguldak escort
adanaescort01.com – adiyamanescortxx.com – afyonarackiralama.net – aksarayescort.net – antalyaoyunpark.com – aydinescortkiz.com – balikesirescortlar.com – batmanescortlar.com – bitlisescortlar.com – burdurescortlar.com – bursamalaysias.com – diyarbakirambar.com – edirnedespor.com – erzurumyolkosusu.com – eskisehirescortlari.com – gaziantepekspres.org – gebzeescortkiz.com – giresunmaraton.com – hataykoleji.com – ispartakpss.com – karabukteknik.com – kastamonuajans.net – kayserivalisi.com – kilisescort.com – kocaeliescortlar.com – konyaescortlar.com – kutahyaizemlak.com – malatyadataksi.com – manisaescortlar.com – marasatasoyemlak.com – mardinfanatik.com – mersinmoda.com – muglaapart.net – nigdeyapi.com – orduescortt.com – osmaniyeyorum.com – sakaryanur.com – samsunescortlar.com – siirteyatirim.com – sincanoto.com – tekirdagescortlar.com – tokatforum.com – usakbasin.com – vanescortilan.com – yalovadaemlak.com – yozgattanal.com – sanliurfadayim.com – zonguldakescort.com
no deposit bonus forex 2021 – takipçi satın al – takipçi satın al – takipçi satın al – takipcialdim.com/tiktok-takipci-satin-al/ – instagram beğeni satın al – instagram beğeni satın al – google haritalara yer ekleme – btcturk – tiktok izlenme satın al – sms onay – youtube izlenme satın al – google haritalara yer ekleme – no deposit bonus forex 2021 – tiktok jeton hilesi – tiktok beğeni satın al – binance – takipçi satın al – uc satın al – finanspedia.com – sms onay – sms onay – tiktok takipçi satın al – tiktok beğeni satın al – twitter takipçi satın al – trend topic satın al – youtube abone satın al – instagram beğeni satın al – tiktok beğeni satın al – twitter takipçi satın al – trend topic satın al – youtube abone satın al – instagram beğeni satın al – tiktok takipçi satın al – tiktok beğeni satın al – twitter takipçi satın al – trend topic satın al – youtube abone satın al – instagram beğeni satın al – perde modelleri – instagram takipçi satın al – instagram takipçi satın al – cami avizesi – marsbahis – betboo
takipçi satın al
takipçi satın al
takipçi satın al
takipçi satın al
takipçi satın al
takipçi satın al
takipçi satın al
takipçi satın al
takipçi satın al
takipçi satın al
takipçi satın al
takipçi satın al
takipçi satın al
takipçi satın al
takipçi satın al
takipçi satın al
takipçi satın al
takipçi satın al
takipçi satın al
takipçi satın al
takipçi satın al
instagram takipçi satın al
instagram takipçi satın al
takipçi satın al
takipçi satın al
instagram takipçi satın al
instagram takipçi satın al
instagram takipçi satın al
instagram takipçi satın al
takipçi satın al
instagram takipçi satın al
https://www.escortsmate.com – adana escort – adıyaman escort – afyon escort – ağrı escort – aksaray escort – amasya escort – ankara escort – antalya escort – ardahan escort – artvin escort – aydın escort – balıkesir escort – bartın escort – batman escort – bayburt escort – bilecik escort – bingöl escort – bitlis escort – bolu escort – burdur escort – bursa escort – çanakkale escort – çankırı escort – çorum escort – denizli escort – diyarbakır escort – düzce escort – edirne escort – elazığ escort – erzincan escort – erzurum escort – eskişehir escort – gaziantep escort – gebze escort – giresun escort – gümüşhane escort – hakkari escort – hatay escort – ığdır escort – ısparta escort – izmir escort – istanbul escort – karabük escort – karaman escort – kars escort
ucuz takipçi
ucuz takipçi
tiktok izlenme satın al
binance güvenilir mi
okex güvenilir mi
paribu güvenilir mi
bitexen güvenilir mi
coinbase güvenilir mi
instagram takipçi satın al
Dachshunds are bred and shown in two sizes: Standard and Miniature. https://www.cutespupsforsale.com/ Standard Dachshunds of all varieties (Smooth, Wirehair, and Longhair) usually weigh between 16 and 32 pounds. Miniature Dachshunds of all varieties weigh 11 pounds and under at teacup poodle for sale maturity. Dachshunds that weigh between 11 and 16 pounds are called Tweenies. Some people who breed exceptionally small Dachshunds advertise them as Toy Dachshunds, but this is purely a poodles for sale marketing term, not a recognized designation. He's bred for perseverance, which is another way of saying that he can be stubborn. Dachshunds have a reputation for being dachshund puppies sale entertaining and fearless, but what they want most is to cuddle with their people. Longhairs are calm and quiet, and Smooths have dachshund for sale a personality that lies somewhere in between. Some Mini Dachshunds can be nervous or shy, but this isn't correct for the breed. Avoid puppies that show these characteristics.Like every dog, Dachshunds need early socialization-exposure to many different people, dachshund puppies for sale near me sights, sounds, and experiences-when they're young. Socialization helps ensure that your Dachshund puppy grows up to be a well-rounded dog. .
The breed became very popular in the early 1900s, and in 1913 and 1914, https://oneshoppharmacy.com they were among the 10 most popular entries in the Westminster Kennel Club Show. During World War I, however, the breed fell on hard times in the U.S. and England because they were poodle for sale closely associated with Germany. Dachshund owners sometimes were called traitors and their dogs stoned. After
World War I, some U.S. breeders dachshunds for sale imported some Dachshunds from Germany and the breed started to become popular once again. The breed faced a similar fate during World War II, but not nearly so severely as during World War I.
In the 1950s, Dachshunds became one of the most popular family dogs in the U.S. again, a status they have enjoyed ever
since. While Dachshunds mini dachshund puppy for sale rarely are used as hunting dogs in the U.S. or Great Britain, in other parts of Europe, especially France, they still are considered hunting dogs. mini dachshund puppies for sale Dachshunds also love a challenge, and as long as you incorporate plenty of opportunities to chase and find things, you’ll miniature dachshund for sale have a happy dog. These dogs love their human parents, and really don’t want them to leave.
The dachshund was bred in Germany hundreds of years ago to hunt badgers. https://www.poodlespring.com/ "Dach" means badger and "hund" means dog. The three varieties of dachshund, smooth-, Dachshund puppies for sale wire-,and long-coated, originated at different times. The smooth was the first and arose from a mixture of a miniature French pointer and a pinscher. The breed also comes in two sizes: standard and miniature, with the standard the original size.
The dachshund has short, strong legs that enable the dog to dig out prey and go inside burrows. Larger versions of the breed were used to chase deer or fox. Smaller dachshunds Dachshund puppy for sale were bred for hunting hares and ferrets.
The breed is still used for hunting, primarily in Europe, nine in dachshunds puppies for sale ches in height.All three types are known
The dachshund's coat may be shades of red, black, chocolate, white or gray. Some have tan markings or are spotted or dappled. Dachshunds live about 12 to 15 years. toy poodle for sale espite their size, dachshunds are known for their courageous nature and will take on animals much larger than themselves. Some may be aggressive toward strangers and other dogs.
As family dogs, dachshunds are loyal companions and good watchdogs. They are good with children if treated well. They can be slightly difficult to train.
Some dachshund fanciers say there are personality differences among the different varieties of the breed. For instance, the long-coat dachshund is reportedly calmer teacup poodles for sale than the smooth-coat variety,
Ahaa, its nice dialogue about this piece of writing at this place at this webpage,
I have read all that, so at this time me also commenting here.
havanese dogs for sale
havanese puppies for sale
teacup havanese puppy
chocolate havanese puppy for sale
havanese puppy for sale
pomeranian puppies for sales
pomeranian for sale
teacup pomeranian for sale near me
pomeranians for sale near me
Hi, I do believe this is a great website. I stumbledupon it 😉 I am going to revisit yet
again since I book-marked it. Money and freedom is the greatest way to
change, may you be rich and continue to help other people.
teacup havanese puppies for sale
teacup havanese puppies for sale
pomeranian teacup for sale
doodle puppies
aussiedoodle puppies for sale
bernedoodle puppies for sale
goldendoodle puppies for sale
ragdoll kitten for sale
ragdoll kittens for sale
Good post. I certainly love this website.
Continue the good work!
mini goldendoodle for sale
mini bernedoodle puppies for sale
mini aussiedoodles for sale
ragdoll cat for sale
ragdoll cats for sale
havanese puppies for sale under $1,000
great dane puppies for sale
great dane puppy for sale
great dane puppies near me
Hi! I could have sworn I’ve been to this website before but after
looking at some of the posts I realized it’s new to me.
Regardless, I’m certainly happy I found it and I’ll be
book-marking it and checking back often!
great dane puppy for sale
great dane puppies for sale near me
goldendoodle for sale
ragdoll kitten near me
ragdoll kittens for sale near me
bernedoodles for sale
aussiedoodle for sale
havanese puppies for sale near me
https://www.redemptionbullies.com/
https://thegorgeousdoodles.com/
https://www.fluffyhavanese.com/
https://thegorgeousragdolls.com/
https://www.pomeranianpuppiesforsales.com/
Just wanted to congratulate you for such an amazing contents,So happy to read your post!
dachshund puppies for sale
dachshund puppy for sale
dachshunds puppies for sale
dachshund puppies sale
dachshund for sale
dachshund puppies for sale near me
dachshunds for sale
mini dachshund puppy for sale
mini dachshund puppies for sale
Please guys let give this blog FIVE STAR Rating
dapple dachshund puppies for sale
miniature long haired dachshund puppies for sale
miniature long haired dachshund for sale
dachshund puppies for sale under $500
long haired dachshund puppies for sale
https://Greenlandpuppies.com
https://oneshoppharmacy.com
I'm happy I came acorss this blog,you are really a content builder,I will be coming back to read more post from you{.
Thanks
toy poodle for sale
poodles for sale
poodle for sale
teacup poodles for sale
teacup poodle for sale
toy poodle for sale near me
poodle for sale near me
mini poodle for sale
poodle puppy for sale
I simply stumbled upon your weblog and desired to say that I have really enjoyed surfing your blog articles.
Positive site, where did u come up with the info on this uploading?
yorkie puppies for sale
teacup yorkie puppies for sale
yorkies for sale
yorkie for sale
yorkshire terrier for sale
yorkie puppy for sale
teacup yorkies for sale
teacup yorkie for sale
yorkie teacup for sale
This Blog Is really informative for us. Thanks For sharing this blog.
Hii this is my first time visiting this web page this blog is really informative for me.
teacup chihuahua for sale
chihuahua puppies for sale
teacup chihuahua puppies for sale
chihuahua for sale
teacup chihuahuas for sale
tea cup chihuahua for sale
chihuahua for sale near me
applehead chihuahua for sale
apple head chihuahua for sale
https://www.yorkiespuppiessale.com/
Heya i'm for the first time here. I came across this board and I find
It truly useful & it helped me out much. I hope to give something back
and help others like you aided me.
yorkies for sale near me
yorkie for sale near me
yorkie puppies near me
yorkies near me
yorkshire terrier for sale
yorkie puppy for sale near me
yorkie puppies for sale near me
teacup puppies for sale near me
teacup yorkie for sale
https://www.chihuahuapuppiesforsale1.com/
Thanks very much for sharing an amazing content with us. we really do appreciate.
teacup yorkies for sale
teacup yorkies for sale near me
yorkie teacup for sale
yorkie puppies for sale
yorkie puppy for sale
teacup yorkie for sale
yorkie for sale near me
teacup yorkie near me
teacup yorkie for sale near me
Nice Post..Thanks for sharing this useful information! This is really interesting information to read.
https://www.newdaypuppies.com/
https://www.myppuphouse.com/
https://www.yorkiespuppiessale.com/
https://www.myppuphouse.com/teacup-maltese-puppies-for-sale/
https://www.myppuphouse.com/teacup-maltipoo-puppies-for-sale/
https://www.myppuphouse.com/teacup-pomeranian-puppies-for-sale/
https://www.myppuphouse.com/teacup-poodle-puppies-for-sale/
https://www.myppuphouse.com/teacup-shih-tzu-puppies-for-sale/
https://www.myppuphouse.com/teacup-yorkie-for-sale/
https://www.newdaypuppies.com/
Please guys let give this blog FIVE STAR Rating
dapple dachshund puppies for sale
miniature long haired dachshund puppies for sale
miniature long haired dachshund for sale
dachshund puppies for sale under $500
long haired dachshund puppies for sale
teacup chihuahua for sale
chihuahua puppies for sale
chihuahua for sale
https://Greenlandpuppies.com
https://oneshoppharmacy.com
seo fiyatları
saç ekimi
dedektör
instagram takipçi satın al
ankara evden eve nakliyat
fantezi iç giyim
sosyal medya yönetimi
mobil ödeme bozdurma
kripto para nasıl alınır
bitcoin nasıl alınır
tiktok jeton hilesi
youtube abone satın al
gate io güvenilir mi
referans kimliği nedir
tiktok takipçi satın al
bitcoin nasıl alınır
mobil ödeme bozdurma
mobil ödeme bozdurma
mmorpg oyunlar
instagram takipçi satın al
Tiktok Jeton Hilesi
tiktok jeton hilesi
antalya saç ekimi
Referans Kimliği Nedir
İNSTAGRAM TAKİPÇİ SATIN AL
METİN PVP
İnstagram takipci satin al
En son çıkan perde modelleri
Mobil onay
mobil ödeme bozdurma
nft nasıl alınır
ankara evden eve nakliyat
TRAFİK SİGORTASİ
dedektör
web sitesi kurma
Aşk kitapları
smm panel
smm panel
iş ilanları
İnstagram Takipçi Satın Al
hirdavatciburada.com
beyazesyateknikservisi.com.tr
servis
tiktok jeton hilesi
bostansepeti.com
site kurma
ürünler
vezirsosyalmedya.com
postegro
sosyal medya yönetimi
surucukursuburada.com
patent sorgula
yorumbudur.com
yorumlar
tiktok jeton hilesi
mobil ödeme bozdurma
mobil ödeme bozdurma
mobil ödeme bozdurma
pubg uc satın al
pubg uc satın al
betboo
süperbahis
1xbet
bedava bonus veren siteler
bonus veren siteler
1xbet
bahigo
anadolucasino
1xbet
sms onay
pdf kitap indir
sanal ofis
https://muhammedsefer.com
If you are interested in purchasing a YouTube account, you can find many reputable companies that sell them online. Make sure to do your research to ensure you are getting a reputable account with a good reputation. youtube account for sale
saasasas
11122121
Nice Content Bro!
Congratulations on your article, it was very helpful and successful. 67a0d0692bd6912ced7c53b8d9884a41
numara onay
website kurma
sms onay
Thank you for your explanation, very good content. 63180cde7da1fb31fa38a418989c6dfd
altın dedektörü
Good content. You write beautiful things.
mrbahis
sportsbet
hacklink
mrbahis
sportsbet
vbet
korsan taksi
hacklink
taksi
Good text Write good content success. Thank you
bonus veren siteler
poker siteleri
mobil ödeme bahis
betmatik
kralbet
betpark
tipobet
slot siteleri